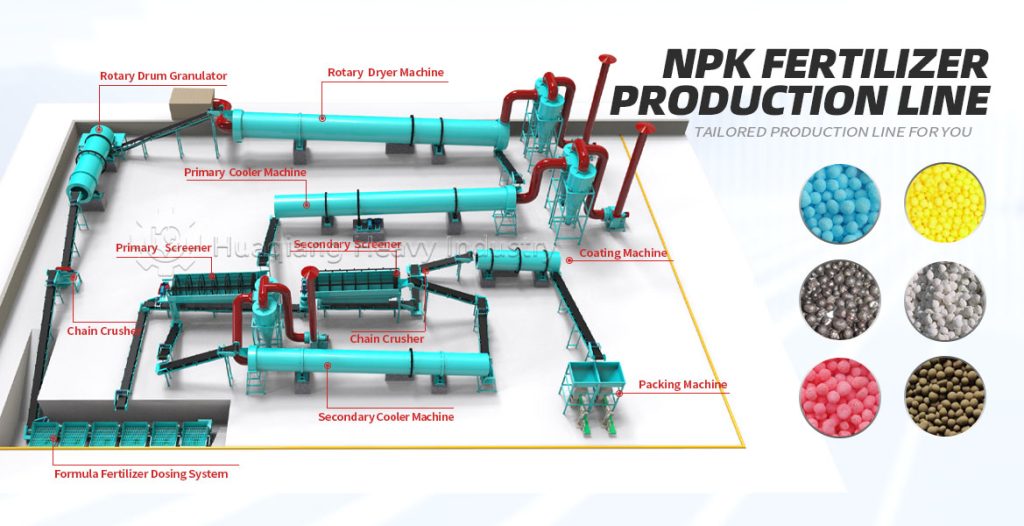
Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are essential macronutrients for plants. NPK fertilizer production lines process them into granular fertilizers using equipment such as rotary drum granulators or disc granulators. However, blindly applying excessive amounts not only fails to promote growth but also disrupts plant physiological metabolism, causing growth problems, leading to reduced yield and quality. The harmful effects of excessive amounts of different elements vary.
Excessive nitrogen fertilizer easily leads to “excessive vegetative growth and poor fruit set” in plants. Excessive nitrogen fertilizer stimulates excessive vegetative growth, resulting in thin stems, dark green leaves, poor ventilation and light penetration, reduced resistance to lodging and pests/diseases, and increased susceptibility to aphids and powdery mildew. In fruits and vegetables, this results in fewer flowers, lower fruit set, deformed fruits, insufficient sweetness, delayed maturity, and compromised quality.
Excessive phosphorus fertilizer causes “nutrient antagonism” and growth stagnation. Excessive phosphorus inhibits the absorption of zinc, iron, and calcium by plants, leading to chlorosis and yellowing of leaves, slow growth of new leaves, and poor root development. Simultaneously, it exacerbates soil compaction, impairs root respiration, and weakens plant growth, with more pronounced harm to calcium- and zinc-loving crops.
Excessive potassium fertilizer causes “physiological imbalance.” Excessive potassium disrupts nutrient balance, inhibits nitrogen and magnesium absorption, and causes leaf edges to scorch and curl, resulting in “leaf burn.” It also affects water transport, reducing plant drought resistance, causing root aging, and hindering fruit enlargement, leading to small or stunted fruit.
In summary, excessive application of granular fertilizer produced by NPK fertilizer production lines will damage plants and pollute the soil in multiple ways. It is necessary to precisely control the nutrient content of granules, rationally manage the amount of fertilizer applied, and follow the principle of “light and frequent fertilization.”